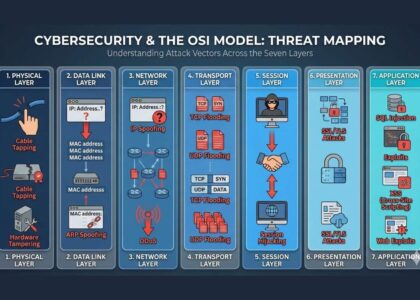
In today’s increasingly connected world, cybercrime is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a global threat impacting individuals, businesses, and governments alike. From phishing emails to ransomware attacks and identity theft, cybercrime is evolving rapidly, targeting our most valuable digital assets.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore:
- What is Cybercrime?
- The major types of cybercrimes
- Real-world examples
- How you can prevent becoming a victim
Table of Contents
- What is Cybercrime?
- Why is Cybercrime on the Rise?
- Types of Cybercrime
- Hacking
- Phishing & Social Engineering
- Ransomware
- Identity Theft
- Cyberstalking & Online Harassment
- DDoS Attacks
- Financial Fraud
- Cyber Espionage
- Real-Life Examples of Cybercrime
- How Cybercrime Affects You
- How to Prevent Cybercrime
- For Individuals
- For Businesses
- Cybercrime Laws and Reporting
- Final Thoughts
What is Cybercrime?
Cybercrime refers to any illegal activity that involves a computer, networked device, or a network. In many cases, cybercrime is committed by hackers or cybercriminals who want to make money, steal data, disrupt services, or spread malware.
Cybercrime can target:
- Personal devices (phones, laptops)
- Business infrastructure (servers, cloud systems)
- Government systems
- Online platforms and social media accounts
Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in software, systems, or human behavior to gain unauthorized access, commit fraud, or sabotage digital systems.
Why is Cybercrime on the Rise?
Several factors contribute to the rise in cybercrime, including:
- Widespread internet access
- Increase in remote work and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device)
- Use of cloud services without adequate security
- Proliferation of smart devices (IoT)
- Lack of awareness among users
- Dark web tools that make cybercrime easier
Cybercrime is appealing to criminals because it’s low-risk and high-reward. Attackers can operate anonymously and from anywhere in the world.
Types of Cybercrime
1. Hacking
Hacking refers to the unauthorized access to or control over computer systems. Hackers may aim to:
- Steal data
- Install malicious software
- Sabotage networks or servers
🔐 Example: A hacker exploiting a zero-day vulnerability to breach a corporate database.
2. Phishing & Social Engineering
Phishing involves sending fraudulent messages that appear to come from a legitimate source. These messages often include malicious links or attachments designed to steal personal or financial information.
Social engineering tricks users into giving away confidential data by manipulating their trust.
📧 Example: An email claiming your bank account will be frozen unless you verify your credentials.
3. Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts files on a victim’s system. The attacker then demands a ransom to restore access.
🦠 Example: The WannaCry ransomware attack affected over 200,000 computers across 150 countries in 2017.
4. Identity Theft
In identity theft, criminals use stolen personal information (like Social Security numbers, credit card details, or medical records) to impersonate someone else for financial gain.
👤 Example: Using someone’s identity to open new credit accounts or claim government benefits.
5. Cyberstalking & Online Harassment
Cyberstalking involves the use of digital platforms to harass, threaten, or intimidate individuals. It often includes repeated, unwanted communication.
💬 Example: Sending abusive messages, doxxing, or leaking private photos online.
6. Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks aim to overwhelm a server, network, or website with traffic, rendering it unusable.
🌐 Example: A group of attackers sending millions of requests to crash a popular e-commerce site during peak hours.
7. Financial Fraud
Cybercriminals target online banking systems, payment platforms, and financial services to commit fraud. This includes unauthorized transactions, account takeovers, and investment scams.
💰 Example: A scammer creating a fake e-wallet app that steals user credentials.
8. Cyber Espionage
Cyber espionage involves unauthorized spying or surveillance through cyber means, often targeting governments, corporations, or political organizations.
🕵️ Example: Nation-state hackers stealing military secrets or trade deals.
Real-Life Examples of Cybercrime
1. Equifax Data Breach (2017)
- Data stolen: 147 million records
- Type: Data breach via unpatched Apache server vulnerability
- Impact: Massive identity theft and lawsuits
2. Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack (2021)
- Type: Ransomware by DarkSide group
- Effect: Gas shortages and a $4.4 million ransom paid
3. Twitter Bitcoin Scam (2020)
- Accounts hacked: Elon Musk, Barack Obama, Apple, etc.
- Type: Social engineering
- Impact: Hackers made over $100,000 in Bitcoin in a few hours
How Cybercrime Affects You
Even if you’re not a big corporation or celebrity, cybercrime can still affect you:
- Financial loss through online fraud or scams
- Reputation damage from hacked social media accounts
- Mental health issues due to cyberbullying or harassment
- Loss of privacy through data leaks and surveillance
- Legal consequences if your system is unknowingly used for criminal activities
How to Prevent Cybercrime
Cybercrime prevention starts with awareness, best practices, and the right tools.
🔒 For Individuals
- Use Strong Passwords
- Use a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Avoid Suspicious Emails and Links
- Don’t click unknown links or download random attachments
- Verify sender identity
- Install Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
- Keep it updated
- Run regular system scans
- Update Your Devices Regularly
- Apply security patches and software updates
- Use Secure Wi-Fi Connections
- Avoid public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions
- Use a VPN when possible
- Monitor Your Accounts
- Set up alerts for unusual activity
- Check credit reports regularly
- Backup Important Data
- Use encrypted cloud backups or external drives
🏢 For Businesses
- Implement a Cybersecurity Policy
- Train employees on safe practices
- Restrict access based on roles
- Secure Your Network
- Use firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and endpoint protection
- Encrypt Sensitive Data
- Both at rest and in transit
- Use MFA and Role-Based Access Control
- Avoid shared accounts and passwords
- Perform Regular Security Audits
- Identify and patch vulnerabilities
- Have a Response Plan
- Prepare for data breaches or ransomware attacks
- Test your disaster recovery process
- Educate Your Staff
- Conduct phishing simulations and workshops
Cybercrime Laws and Reporting
Governments worldwide are cracking down on cybercrime with robust laws:
- India: IT Act 2000 (Amended 2008), Cybercrime cells in every major city
- USA: Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA), FBI Cyber Division
- UK: Computer Misuse Act 1990
- Global Bodies: INTERPOL, Europol’s EC3
How to Report Cybercrime
- India: cybercrime.gov.in
- USA: ic3.gov
- UK: actionfraud.police.uk
- Report to local police or cybersecurity helplines
Final Thoughts
Cybercrime is a growing threat, but with the right precautions and awareness, you can protect yourself and your digital assets. Whether you’re an individual scrolling through social media or a business owner handling customer data, cybersecurity is everyone’s responsibility.
✅ Key Takeaways:
- Always keep your software updated.
- Never share personal details over email or unknown calls.
- Use strong, unique passwords for every platform.
- Stay educated on current threats and scams.
By staying alert and proactive, you can stay several steps ahead of cybercriminals. Don’t wait until it’s too late—start protecting yourself today.